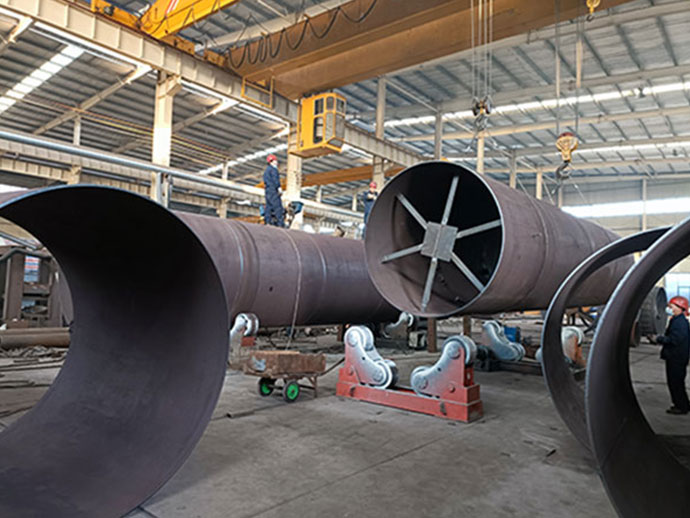
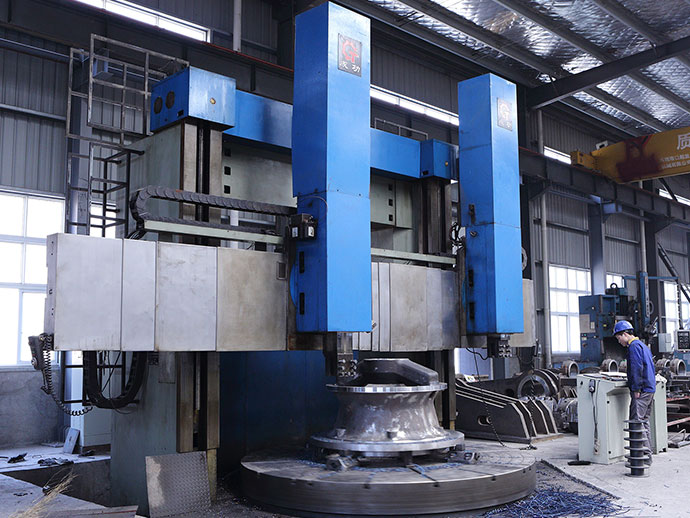
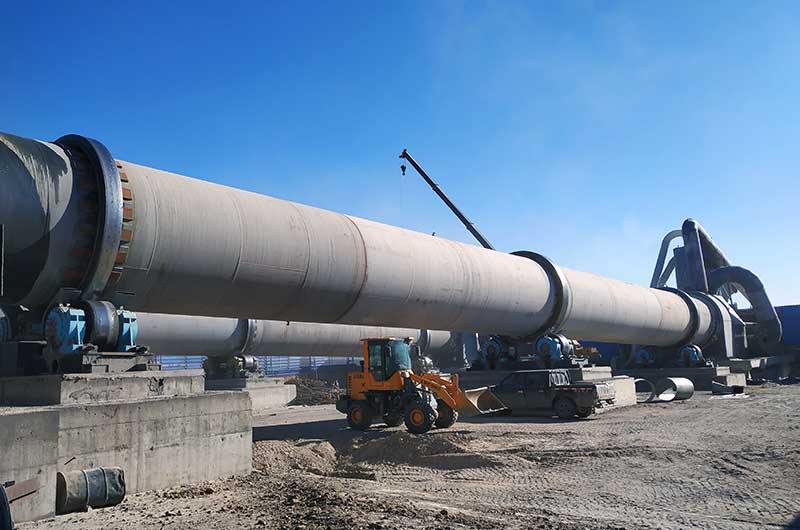
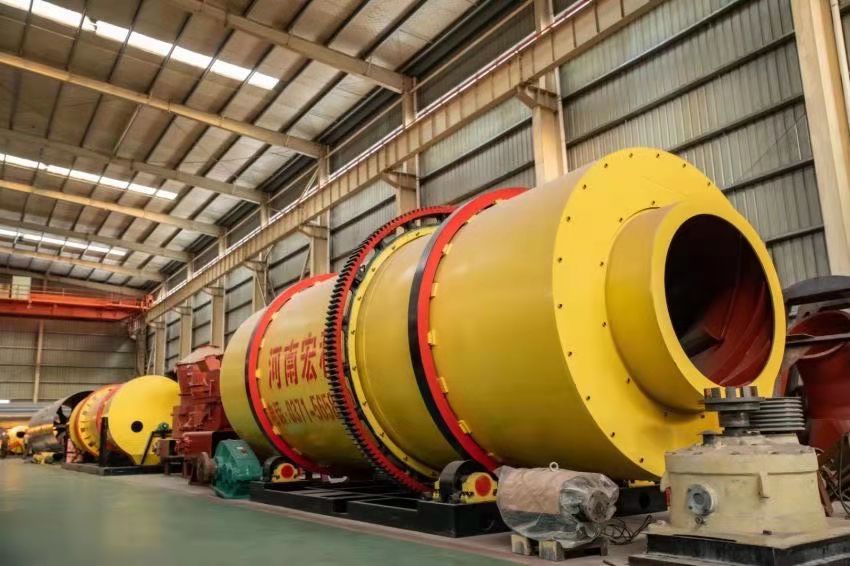
Rotary kiln refers to rotary calcining kiln which belongs to building material equipment. According to the material types to be processed, rotary kiln can be divided into cement rotary kiln, metallurgical chemistry kiln and limestone rotary kiln.
Concrete Category and Function of Rotary Kiln
Cement kiln is mainly used for calcining cement clinker which can be divided into dry-producing cement kiln and wet-producing cement kiln.Metallurgical chemistry kiln is mainly used for the magnetizing roasting of the lean iron ore and the oxidizing roasting of the chromium and josephinite in the steel works of metallurgical industry, for the roasting of high alumina bauxite ore in the refractory plant, for the roasting of clinker and aluminium hydroxide in the aluminium manufacturing plant and for the roasting of chrome ore in the chemical plant.Limestone kiln is mainly used for roasting active lime while lightly calcined dolomite used in the steel works and ferroalloy works.
Brief Introduction of Rotary Kiln
Rotary kiln (cement kiln) is used for making of cement clinker and there are dry and wet methods to make cement.
Rotary kiln (metallurgy chemical) kiln is used for magnetic roasting of iron ore and oxidizing roasting of chrome and nickel in the steel factory.
Rotary kiln is used for baking high-alumina mine in the refractory material factory.
Rotary kiln is used for baking alumina in the aluminum factory and baking chrome ore and chrome powder in the chemical plant.
Rotary kiln (lime kilns) is used for baking active lime and dolomite in the steel factory and ferroalloy factory.
Technical Data
| Product specifications (m) | Kiln dimensions | Capacity (t/d) | Rotation speed (r/min) | Motor power (kw) | Total weight (t) | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter(m) | Length(m) | Obliquity(%) | ||||||
| Φ2.5×50 | 2.5 | 50 | 3 | 200 | 0.62-1.86 | 55 | 187.37 | ---- |
| Φ2.8×44 | 2.8 | 44 | 3.5 | 400 | 0.437-2.18 | 55 | 201.58 | Outside disassemble kiln |
| Φ3.0×45 | 3 | 45 | 3.5 | 500 | 0.5-2.47 | 75 | 210.94 | ---- |
| Φ3.2×50 | 3.2 | 50 | 4 | 1000 | 0.6-3 | 125 | 278 | Outside disassemble kiln |
| Φ3.5×54 | 3.5 | 54 | 3.5 | 1500 | 0.55-3.4 | 220 | 363 | Kiln with preheater precalcine |
| Φ4.0×56 | 4 | 56 | 4 | 2300 | 0.41-4.07 | 315 | 456 | Kiln with preheater precalcine |
| Φ5.0×74 | 5 | 74 | 4 | 6000 | 0.35-4 | 710 | 944 | Kiln with preheater precalcine |
| Φ6.0×95 | 6 | 95 | 4 | 10000 | Max5 | 950×2 | 1659 | Kiln with preheater precalcine |
China Professional Rotary Kiln Manufacturer